The air cooling and heating system heat pump is an efficient and energy-saving air conditioning equipment that can provide heating in winter and cooling in summer, with strong adaptability and flexibility. The operating principle of the air energy refrigeration and heating system heat pump is to use the working principle of the heat pump cycle to achieve refrigeration or heating through the heat transfer of the circulating fluid.
The air energy refrigeration and heating system heat pump consists of an evaporator, compressor, condenser, expansion valve, etc. The evaporator and condenser correspond to indoor and outdoor respectively, while the compressor and expansion valve are the two key components connecting the evaporator and condenser.
The working principle of the heat pump cycle is as follows:
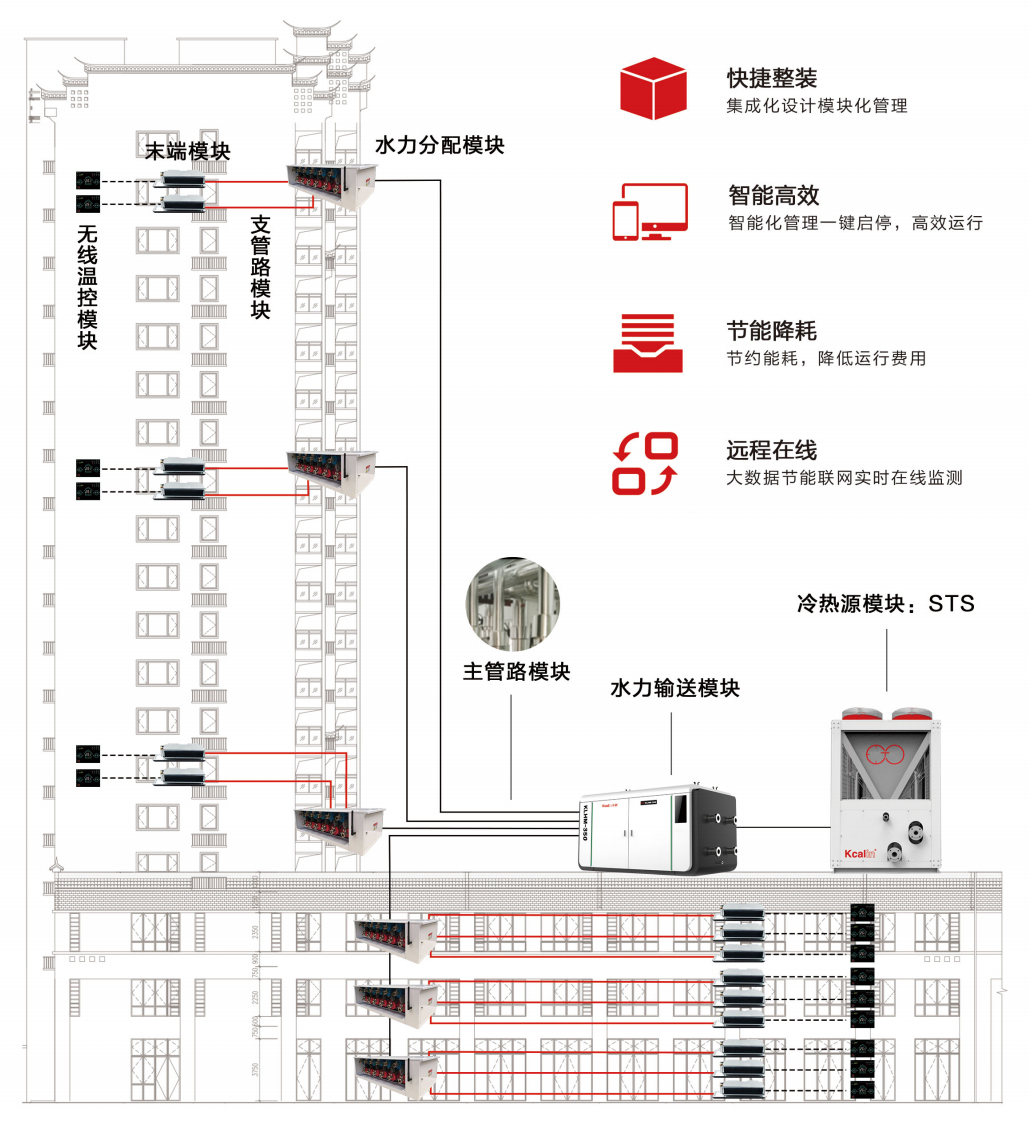
Evaporator: The cycle of the heat pump begins with the evaporator, which is the indoor part of the heat pump. The evaporator is filled with refrigerant. When the refrigerant flows through the evaporator, it absorbs heat from the indoor air, causing the temperature of the evaporator to decrease, resulting in a decrease in indoor temperature.
Compressor: The refrigerant passing through the evaporator enters the compressor in the form of gas. The compressor compresses the gas into a high-pressure and high-temperature state, increasing the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant.
Condenser: The compressor delivers high-pressure and high-temperature refrigerant to the condenser, which is the outdoor part of the heat pump. The air flowing through the condenser is outdoor air, and the refrigerant releases heat, causing the temperature of the condenser to increase and the temperature of the outdoor air to decrease. The refrigerant gradually turns into a liquid in the condenser.
Expansion valve: The refrigerant passes through the condenser and becomes a liquid. After passing through the expansion valve, the refrigerant pressure drops sharply, reducing the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant, causing it to return to a gaseous state, and the cycle begins.
The above is the operating principle of a heat pump in an air cooling and heating system. It utilizes the working principle of a heat pump cycle to convert the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air into indoor cooling or heating needs, achieving efficient and energy-saving cooling and heating. The air energy refrigeration and heating system heat pump has the following characteristics:
Efficient and energy-saving: During the heat pump cycle, there is no need to consume a large amount of electrical energy like traditional air conditioning systems for direct cooling or heating. Instead, the heat in the air is used for heat exchange, greatly reducing energy consumption.
Environmental protection and energy conservation: The operation of the air cooling and heating system heat pump does not produce harmful gases and pollutants, which not only meets environmental requirements but also reduces the impact of the environment on air quality and health.
Can adapt to different environments: Air cooling and heating systems with heat pumps can adapt to different environments, providing suitable cooling or heating services both in summer and winter.
High flexibility: The air cooling and heating system heat pump is not limited by space and can be installed inside or outside the house, making space usage more flexible.
Overall, the air energy refrigeration and heating system heat pump is an efficient, environmentally friendly, energy-saving, adaptable, and highly flexible air conditioning equipment, which is expected to become the mainstream choice for future home and commercial air conditioning.






Comment